How to Select Tube Fittings: A Complete Guide to Materials, Threads, and Size Selection?
2025-10-30
Featured Products
Applications and Advantages of Tube Fittings
Tube fittings are widely used in petrochemical, gas, and process control systems to connect various types of metal tubing. Without the need for welding, they achieve a strong and reliable seal with the following major advantages:
- Excellent Leak Prevention: The double-ferrule design forms a gas-tight seal by gripping the tube wall securely, effectively preventing fluid or gas leakage. This torque-free sealing mechanism eliminates potential leak risks within piping systems.
- Quick and Easy Installation: Installation requires only a wrench to tighten the nut. All forces are applied axially along the tube without rotational stress, and no special tools are required. JPE fittings up to 1-inch size can be quickly assembled with common hand tools, ensuring convenient field installation.
- Reusable and Serviceable: High-quality tube fittings can be reassembled multiple times while maintaining reliable sealing performance (provided the line is depressurized). This makes system maintenance and modifications flexible and cost-effective.

Specification Features of JPE Tube Fittings
As a professional manufacturer of instrumentation tube fittings, JPE provides a complete range of specifications to meet diverse engineering requirements:
- Wide Size Range: Covers both metric and inch sizes, suitable for tubing with outside diameters from 1/16" to 1" (approximately 3 mm to 25 mm). Whether for small instrumentation tubing or large industrial lines, there is a matching JPE fitting size.
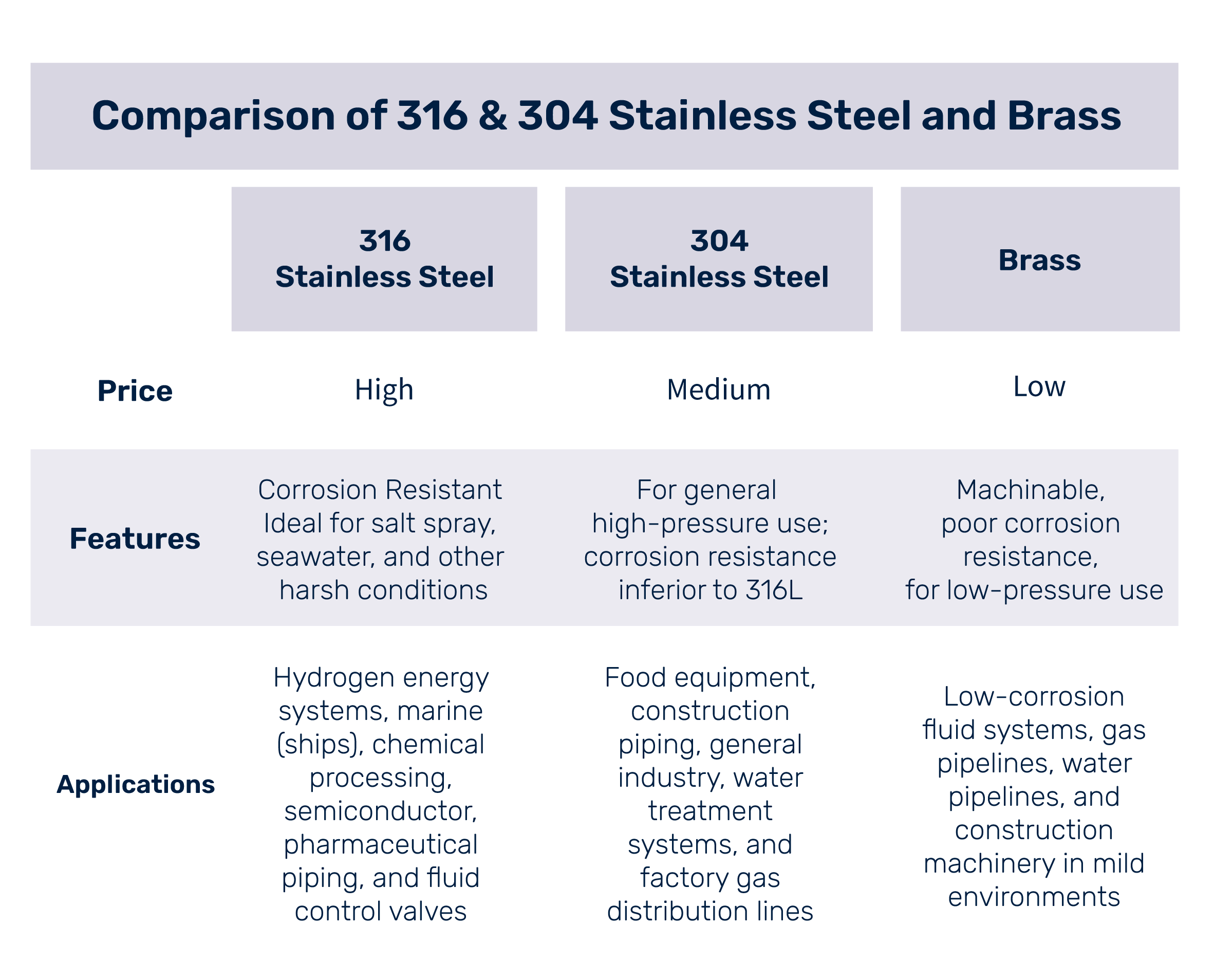
- Various Material Options: Standard materials include 316L stainless steel, 304 stainless steel, and brass, balancing corrosion resistance with cost efficiency. For harsh environments, JPE fittings ensure long-term reliability under demanding conditions.
- Comprehensive Thread Types: Multiple thread standards are available, including NPT (U.S. tapered), BSPT (British tapered), and BSPP (parallel) threads, meeting different international piping standards. JPE offers both male, female, and straight thread configurations to suit various equipment interfaces.
It is worth noting that JPE tube fittings demonstrate outstanding precision manufacturing and quality control. Each fitting consists of four precisely machined components — nut, front ferrule, back ferrule, and body — all produced under strict tolerance control to ensure perfect fit and consistent sealing even under high pressure and vibration conditions.

Quick Selection Guide: Material and Size Choice
When selecting tube fittings, consider the following key factors to quickly identify the proper material and size:
- Material Selection by Medium / Environment / Temperature / Pressure: Choose material based on fluid corrosiveness and operating conditions. For corrosive or high-pressure gases, use 316L stainless steel or equivalent high-strength materials. For low-pressure, non-corrosive media such as oil or water, brass fittings offer a cost-effective alternative. Ensure the tubing hardness is lower than the fitting material to avoid sealing failure (e.g., avoid using stainless-steel tubing with brass fittings).
- Verify Tube Outer Diameter: Fitting sizes are defined by tube outside diameter (OD). The fitting must exactly match the tube OD to ensure proper sealing. Always measure and confirm before ordering. For example, a 6 mm tube should use a 6 mm fitting, and a 1/4" tube should use a 1/4" fitting.
- Check Tube Wall Thickness: For high-pressure or gas applications, ensure sufficient wall thickness. Gas molecules are small and can leak through micro-gaps in thin-wall tubing. For gas systems, always use thick-wall tubing to maintain safety and sealing integrity. Refer to manufacturer recommendations for minimum wall thickness.
- Match Thread Type to Equipment: Verify the thread standard of the equipment port and select a compatible fitting. Use NPT for American systems and BSP series for British systems. Proper thread type and dimension matching prevent loosening and leakage.
Following these guidelines helps narrow down the selection efficiently, ensuring the right fitting is chosen the first time and preventing installation or maintenance issues later.
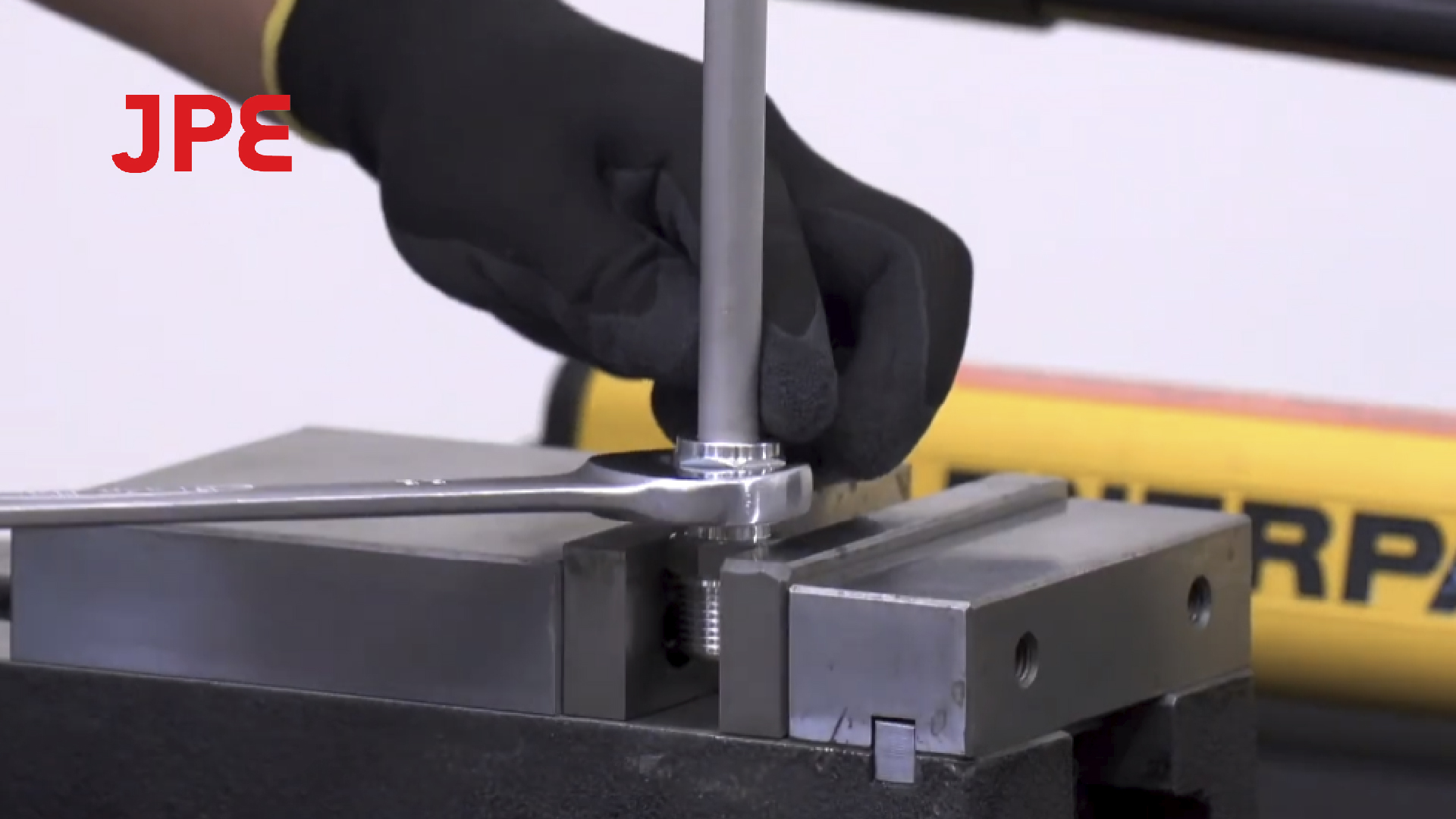

Common Misconceptions and Correct Practices
During the selection and application of tube fittings, beginners often have some misunderstandings. Below are two common misconceptions clarified:
Misconception 1: Tube fitting size is based on inner diameter.
Correct: Tube fitting sizes correspond to the tubing’s outer diameter (OD), not the inner diameter. The ferrule grips the tube’s outer wall to achieve sealing; if the size does not match the OD, proper sealing cannot occur. Always select fittings based on tube OD — never substitute with approximate dimensions.
Misconception 2: Thin-wall tubing is acceptable for gas applications.
Correct: Gases have high permeability and low viscosity, making them prone to leakage through deformed or unsealed interfaces. Thin-wall tubing can deform under ferrule pressure, leading to leaks. Always use thick-wall tubing in gas service to enhance strength and sealing reliability. This is a critical principle in gas-line design.
With the above guidelines and clarifications, you should now have a clear understanding of JPE tube fittings’ dimensional standards and selection principles. For further product details or technical assistance, please contact the JPE team. Our engineers will recommend the most suitable solution to ensure safety and reliability for your fluid systems.
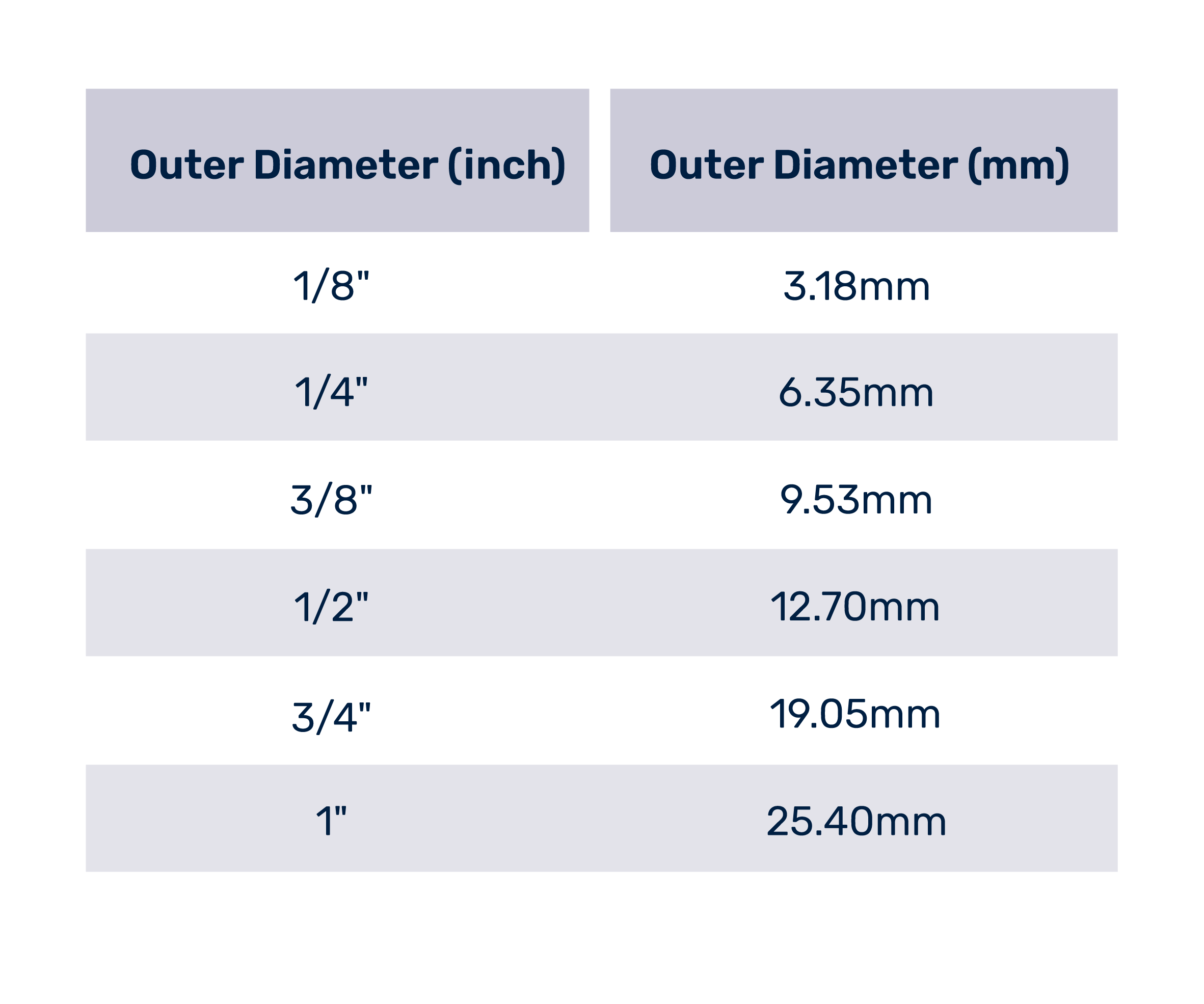
Tube Fitting Size Chart (Inch–Metric Conversion)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can JPE tube fitting components be interchanged with other brands?
A: It is not recommended to mix and match components from different brands. Each manufacturer may have different tolerances and design geometries for the nut, ferrule, and body. Mixing parts creates an untested assembly, potentially leading to mismatched sealing surfaces, unpredictable leakage, or safety risks. For optimal reliability, always use complete fittings from the same brand.
Q: Can 6 mm tubing be used with 1/4" tube fittings?
A: Not recommended. Although 6 mm is approximately equal to 1/4 inch (6.35 mm), they are not identical. Forcing a 6 mm tube into a 1/4" fitting may prevent proper ferrule grip and result in leakage or disconnection. The correct practice is to use matching sizes — 6 mm tube with 6 mm fitting, and 1/4" tube with 1/4" fitting — to ensure reliable sealing.